Prostatitis is a disease of the prostate gland (prostate), developed as a result of inflammatory changes in it. According to statistics, the prevalence of the disease reaches 35 to 50%, and is revealed to men in the age of 20-40 years.
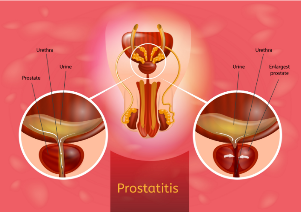
Types of
Distinguished 4 forms of prostatitis:
- acute (bacterial);
- chronic bacterial;
- chronic non-bacterial;
- asimptomaticheskiy chronic.
Acute prostatitis is rare due to the swift current of the inflammatory process and immediate transition into the chronic stage (the fake upgrade).
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, otherwise it is called a syndrome of chronic pelvic pain, can have an inflammatory reaction (with the presence in the urine and the ejaculate of an increase of white blood cells) and non-inflammatory nature.
The causes of the
The cause of acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis are the pathogenic micro-organisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi). Often the source of inflammation are:
- e. coli;
- streptococci;
- staph;
- protey;
- klebsiella;
- pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- the causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia, mikoplazmi, gonorrhea, trichomonas, cytomegalovirus, and others).
The greater part of the microorganisms found in the intestine, in the epidermis of the skin, but falling in the tissue of the prostate that causes an inflammatory process. As a general rule, the cause of the disease is not a stimulant, and the association of several types of microbes.
The development of the chronic prostatitis can cause the following factors:
- diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- the sedentary lifestyle ("sedentary" work);
- the tendency to constipation;
- the weakening of the body's defenses;
- of the injury;
- the hormonal imbalance;
- the abuse of alcohol and smoking;
- disordered sexual relations;
- transient sexual life (a prolonged period of abstinence);
- interruption of the sexual act;
- irregular emptying of the bladder;
- unsatisfied sexual desire;
- chronic stress;
- the supercooling;
- the presence of tooth decay and other sources of chronic infection (eg, chronic tonsillitis).
The symptoms of prostatitis
Acute prostatitis - a very insidious disease. "Take" is quite difficult, because, in the first place, the process is very fast becomes chronic, and in the second place, the majority of patients prefer to "expired" manifestations of acute prostatitis of the house. Your doctor of patients with inflammation of the prostate often direct as in the case of erection disorders and other consequences.
The acute form of the disease happens in the background:
- increase of the temperature;
- chills;
- other signs of intoxication (weakness, lethargy, loss of appetite, etc).
The inflammation of the prostate gland accompanied by pain in the groin, in the groin and on the scrotum.
It is characteristic also of the painful and the increase in the frequency of urination. Sometimes in the urine, you may notice a whitish purulent.
In addition, the patient can pay attention to the lack of night life and of erections, poor erection at the time of the intimacy and the strong shortening of the sexual relationship.
The signs of chronic bacterial prostatitis may not exist or appear in the periods of exacerbation. This stage is characterized by pain in the groin and in the lower part of the abdomen, which often radiates to the sacrum, the kidneys and the scrotum.
Appear the typical symptoms of disorders of urination: urine stream weak and frequent urge, even though most of the urine is separated a little.
Hereinafter, for the lack of treatment of chronic prostatitis, reaches the peak: there are disorders of the sexual function. For example:
- the lack of erection or the lack of it;
- painful erections, due to which the patient refuses to have sex;
- effacement orgasm;
- short the sexual act;
- the pain of the ejaculation.
Leaves much to be desired and the general state of men: he is fatigued quickly, constantly annoyed, poor sleep.
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis is of 95% between all of the prostate, you are sick I was a predominance of men of approximately 30 years. It is characterized by permanent or periodic pain in the pelvic area, prostate, scrotum, this analysis does not there are signs of inflammation. The cause of the disease is not exactly that are installed.
The diagnosis
In the diagnosis of acute prostatitis and chronic, in addition to the collection of complaints, medical history and examination of the patient using the following methods:
- the general analysis of blood and urine;
- the research microscpica of the secretion of the prostate, and the planting in broth culture for the detection of the pathogen (the secret received after the thumb massage of the prostate through the rectum);
- cytologic screening of the urine;
- Ultrasound of the prostate and the organs of the pelvis;
- the computed tomography and the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (mri);
- a sample from the urethra in the microflora.
The differential diagnosis focuses on the distinction of prostatitis, adenoma of prostate, cancer of prostate, the signs of stones in the prostate.
The full list of diagnostic procedures and drugs for the treatment of prostatitis in the Federal standard of care, 2012.
The treatment of prostatitis
The same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not be by the textbook. Do not try to heal themselves, check with your doctor.
The treatment of prostatitis takes the surgeon-urologist.
The goal of causal treatment, with the aim of removing the cause of the prostatitis, is the elimination of the pathogen. In function of the determination of the cause were assigned to the antibiotics, antiviral, or antifungal. The duration of therapy acute prostatitis is 7-10 days, when chronic for 4 to 8 weeks.
For the treatment of a bacterial infection that is used:
- antibiotics fluoride quinoline series (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin);
- the macrolides (erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- doxycycline;
- antibacterial drugs.
Anti-fungal are appointed by the oral route, and in the light of the candles.
In addition, you use other types of therapy:
- anti-allergic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- the relief of pain.
It is also assigned:
- physical therapy;
- gymnastics;
- prostate massage.
The full course of treatment lasts 3-4 months.
Complications
Not cured prostatitis danger of the following complications:
- the obstruccin of the bladder with the follow-up of acute urinary retention;
- infertility;
- recurrent inflammation of the bladder;
- abscess of the prostate;
- depression;
- impotence;
- the adenoma of the prostate;
- calculous prostatitis (stone similar with debilitating pain);
Prognosis
Prognosis acute prostatitis favorable, early treatment leads to a full recovery. The frequency of acute episodes of chronic prostatitis reaches 50% or more, but if it supports the treatment, you can achieve the support of the remission.
The prevention of the
For the prevention of the disease, it must comply with the following conditions:
- regular sexual life with the constant companion;
- the rejection of bad habits;
- healthy living (sport, outdoor walks);
- the compliance of the diet;
- regular attendance to a urologist.































